Unifying Context Ranking and Retrieval-Augmented Generation with RankRAG
More videos are coming out! Stay tuned! 🤓
Large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly powerful tools for tackling a wide range of knowledge-intensive natural language processing (NLP) tasks. One such technique that has gained significant attention is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which combines the strengths of LLMs with the ability to retrieve relevant information from external sources.
In the standard RAG pipeline, a standalone retriever first extracts the top-k most relevant contexts from a large corpus, which are then fed into the LLM to generate the final answer. While this approach has shown promising results, it faces several limitations that can hinder its performance.
Limitations of top-k chunks approach
One key challenge is the trade-off in selecting the optimal number of retrieved contexts (k). A smaller k may fail to capture all the relevant information, compromising the recall, while a larger k can introduce irrelevant content that hampers the LLM’s ability to generate accurate answers. Additionally, the limited capacity of the retriever, often a moderate-sized model, can constrain its effectiveness in accurately matching the question to the relevant documents, especially in new tasks or domains.
RankRAG
To address these limitations, researchers at NVIDIA have proposed a novel framework called RankRAG, which instruction-tunes a single LLM for both context ranking and answer generation in the RAG pipeline. By unifying these two crucial components, RankRAG aims to enhance the LLM’s overall capability in knowledge-intensive tasks.
The key innovation of RankRAG lies in its two-stage instruction tuning process. In the first stage, the LLM undergoes supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on a blend of high-quality instruction-following datasets, including conversational datasets, long-form QA, and LLM-generated instructions. This stage equips the LLM with basic instruction-following capabilities.
In the second stage, RankRAG expands upon the SFT data by incorporating context-rich QA, retrieval-augmented QA, and ranking datasets. This specialized instruction tuning enables the LLM to effectively filter out irrelevant contexts during both the retrieval and generation phases of the RAG framework.
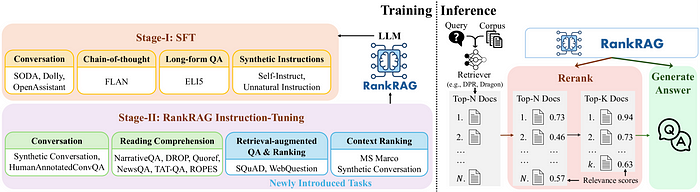
Remarkably, the researchers found that integrating a small fraction of ranking data into the instruction tuning blend works surprisingly well, even outperforming LLMs fine-tuned with 10x more ranking data. This data-efficient approach is attributed to the transferable design of the RankRAG training, where the ranking data closely resembles the general RAG fine-tuning data.
Performance
The authors extensively evaluated RankRAG on a diverse set of knowledge-intensive benchmarks, including open-domain QA, fact verification, and conversational QA tasks. Across nine general-domain and five biomedical datasets, RankRAG demonstrated significant improvements over state-of-the-art RAG models, such as ChatQA-1.5, as well as other strong baselines.
For example, on the challenging PopQA dataset, which focuses on long-tailed entities, RankRAG 8B outperformed ChatQA-1.5 8B by more than 10 percentage points in exact match (EM) score. Similarly, on the multi-hop HotpotQA dataset, RankRAG 8B achieved a 35.3% EM score, compared to 33.4% for ChatQA-1.5 8B.
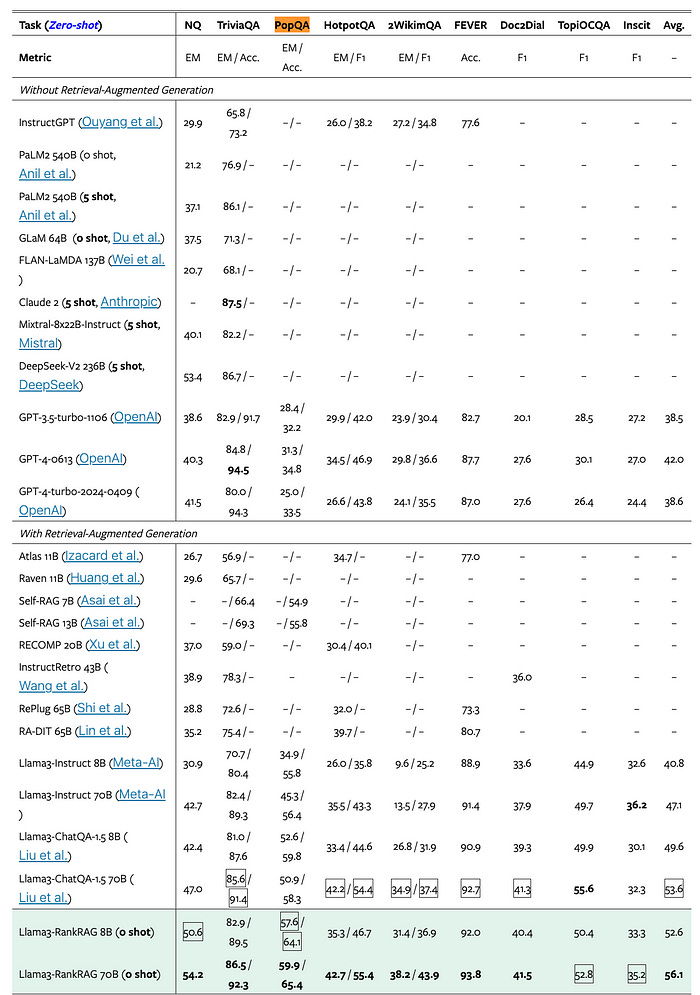
The authors also showcased RankRAG’s robustness to different retrieval models,
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The MLnotes Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.

