RAG in 2024: State of the Art and the Path Forward - Recap from GenAI Summit
Insights from Tengyu Ma - RAG expert and Stanford professor
Introduction
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a dominant approach in the field of natural language processing, particularly for enterprises looking to leverage large language models while incorporating their proprietary information.
In this blog post, we'll explore the current state of RAG in 2024, based on insights from Professor Tengyu Ma's recent talk at the GenAI Summit this weekend, and examine the potential future directions for this technology.
We’ll answer 3 main questions today:
Is RAG still worth it when there’s long context models and fine-tuning options?
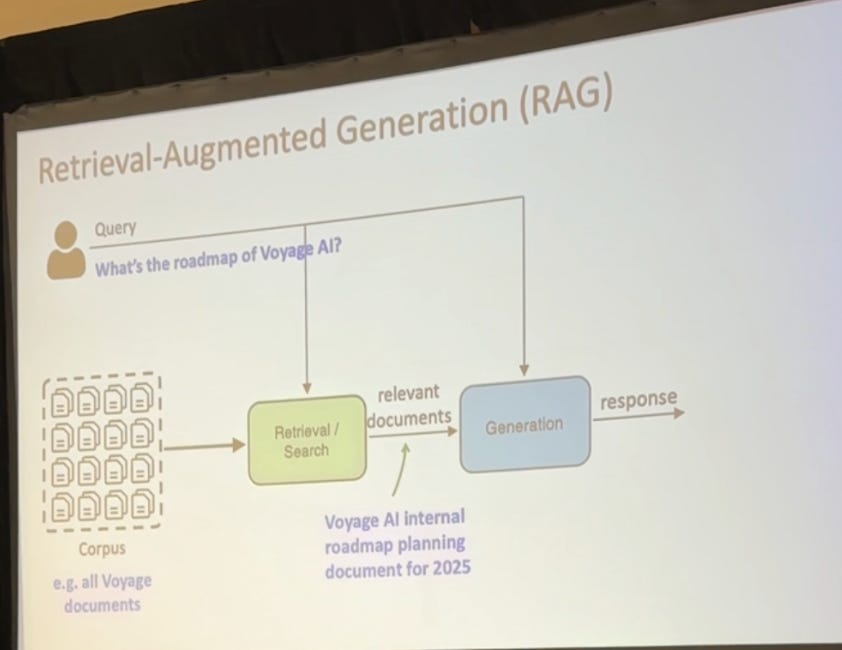
What’s the current RAG landscape?
What will the future look like?
The RAG Advantage
RAG has gained significant traction over competing approaches like fine-tuning and long context transformers. The primary reason for this is its ability to efficiently incorporate external knowledge without the need to retrain or significantly alter the base language model.
RAG vs. Fine-tuning and Long Context Transformers
Long Context Transformers: While powerful, these models require reading the entire "library" of information for each query, resulting in high computational costs and potential loss of relevant information.
Fine-tuning: This approach "rewires" the model to incorporate new information but faces challenges with data quality requirements and difficulty in updating or removing knowledge.
RAG: Mimics human problem-solving by retrieving relevant information before generating a response. It's modular, fast, and cost-effective, with the added benefit of reducing hallucinations by grounding responses in retrieved data.
In a nutshell, we believe RAG is here to stay. Ultimately, solving problems efficiently, economically, and sustainably is core to human innovation, and RAG-enhanced technologies align perfectly with this drive.
Current State-of-the-Art RAG Techniques
Several techniques are being employed to enhance RAG performance:
If you’d like to learn more about these techniques, check out our YouTube Channel!
1. Hybrid Search and Reranking
This approach combines multiple search methods (e.g., embedding-based and keyword-based) and uses a reranker to improve result relevance.
2. Query and Document Enhancement
Query Decomposition: Expanding or rephrasing queries to improve retrieval accuracy.
Document Enrichment: Adding contextual information to document chunks to preserve global context.
3. Domain-Specific Customization
Tailoring embedding models for specific domains like law, finance, or code to improve retrieval performance in specialized areas.
4. Custom Parsers and Text Extractors
Developing specialized tools for parsing different data formats (e.g., PDFs, images) and extracting meaningful text for embedding.
5. Embedding Model Fine-tuning
Adapting embedding models to specific libraries or datasets to improve semantic search capabilities.
6. Contextualized Retrieval
Generating context for document chunks using large language models to enhance retrieval accuracy. See our recent post for more details:
The Role of Embedding Models
The quality of retrieval in RAG systems heavily depends on the performance of embedding models. Recent advancements have shown steady improvements across various domains, but there's still room for growth.
Challenges in Current RAG Systems
Despite its advantages, RAG still faces some challenges:
Complexity of implementation, with multiple "tricks" required for optimal performance.
The need for domain-specific customizations.
Balancing retrieval accuracy with computational efficiency.